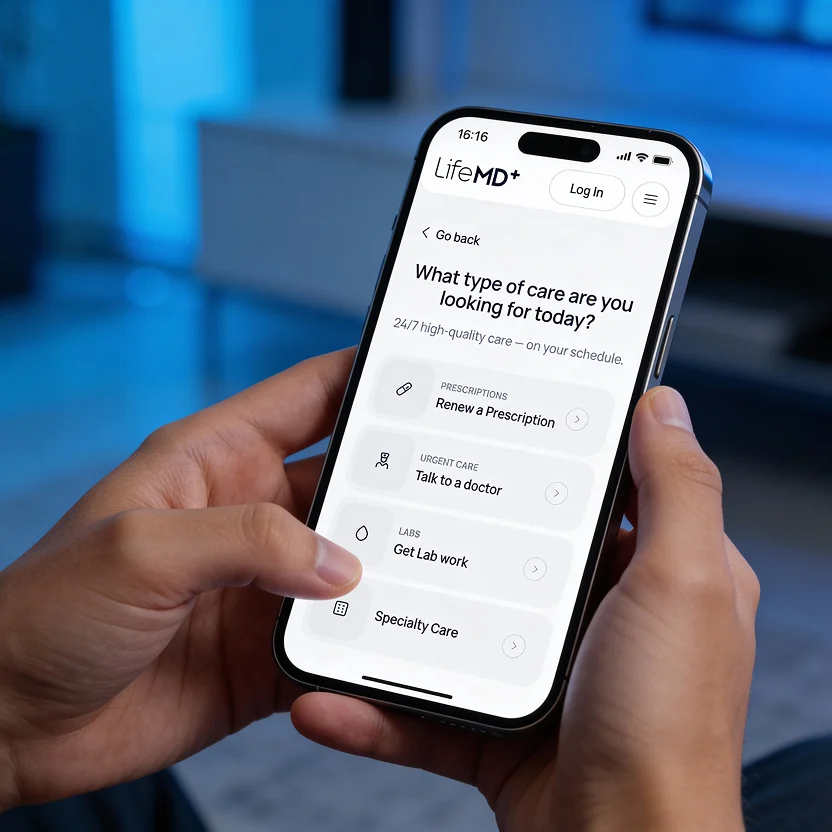
Schedule
Book a telehealth appointment from wherever you are. No insurance necessary.
Achieve your weight-loss goals with GLP-1 treatments like Wegovy® and Zepbound®, guided by licensed providers every step of the way.
Personalized care for women, with HRT and lifestyle support to ease menopause symptoms and restore balance.
Simple, supportive mental health care on your terms, including access to prescription medication when appropriate.
Connect with board-certified cardiologists to help manage blood pressure, cholesterol, and long-term cardiovascular risk — from the comfort of home.
Care without the wait—connect 24/7 with licensed providers for same-day prescription refills and common concerns like colds, flu, rashes, and more.
Talk to a doctor anytime, anywhere — 24/7 urgent & primary care with a telehealth visit in under one hour.
Get your medication prescribed online and sent same-day to your local pharmacy for pickup.
Save time, money, and the hassle — no in-person visits or insurance required.


Prescription treatments are tailored to your specific condition, ensuring effective relief.

Urgent evaluation is crucial to identify your condition early and prevent complications.
Accurate testing, if needed, can confirm your diagnosis and guide the best course of treatment

Licensed providers can send prescriptions to your local pharmacy within an hour, day or night.
step 1
Book a telehealth appointment from wherever you are. No insurance necessary.

step 2
Meet with a board-certified doctor or nurse practitioner from your mobile device.

step 3
Get a prescription if needed (save up to 90%), and pick it up at your pharmacy.
Bronchitis is an inflammation of the lining of the bronchial tubes, which carry air to and from the lungs. Bronchitis can cause someone to cough up thickened (sometimes discolored) mucus. Wheezing is common as well. Bronchitis can be either acute or chronic, and requires treatment from a doctor.
Get Started Get Started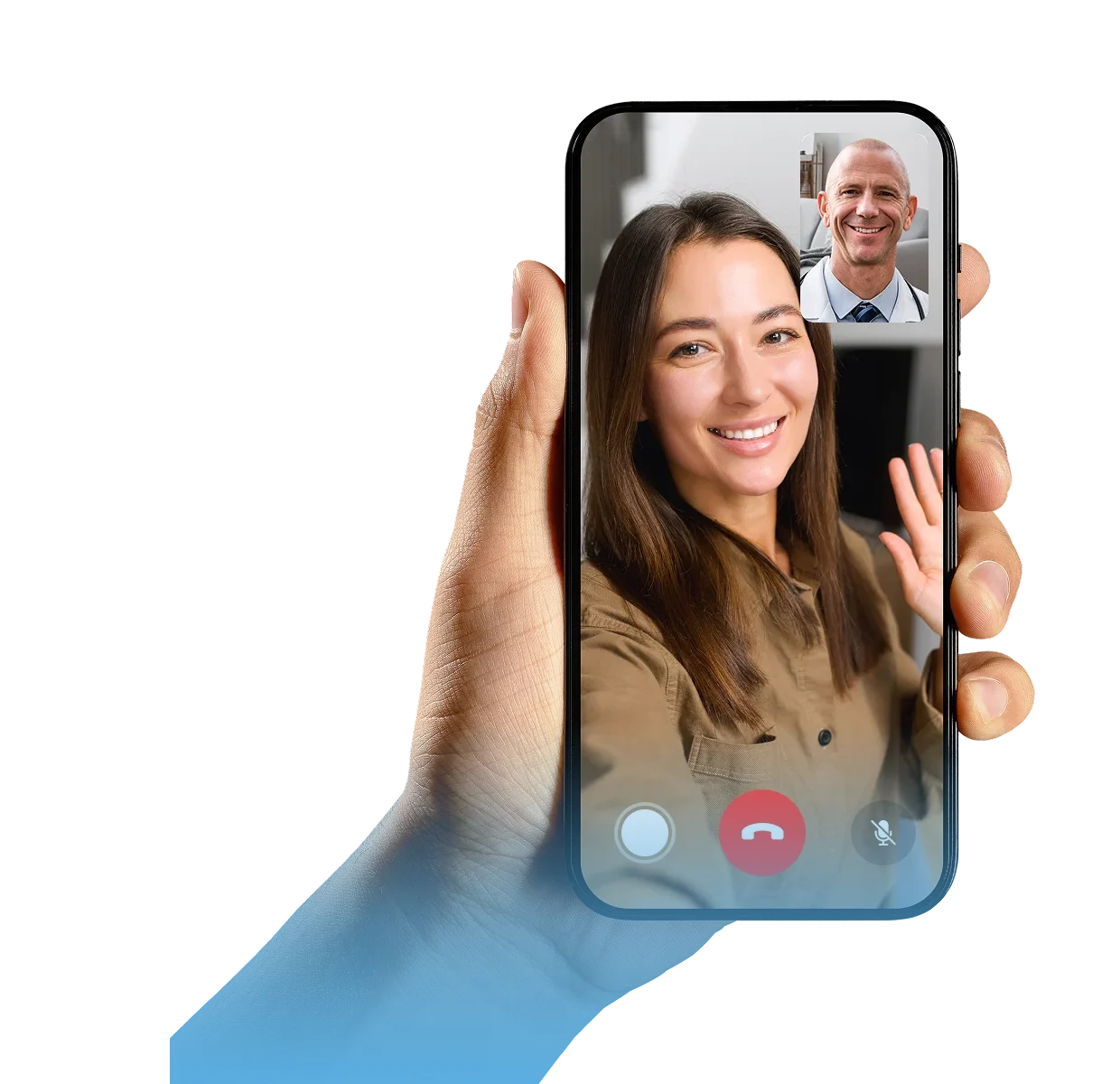
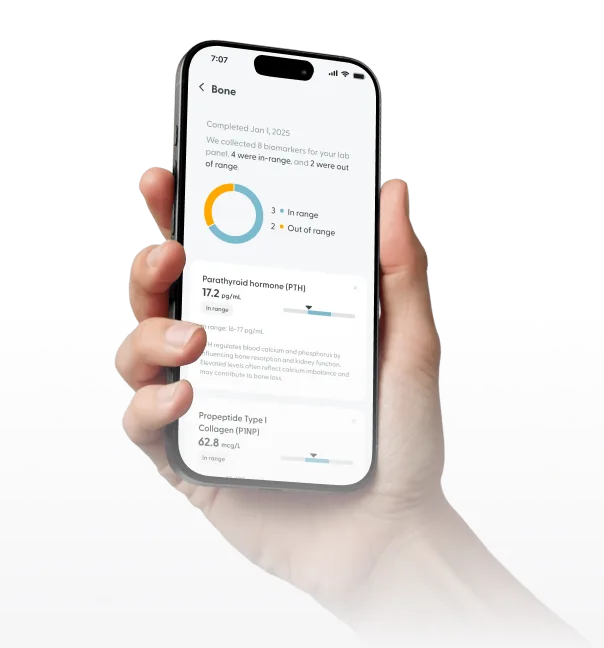
Total Cholesterol

37 mg/mL
In range

LDL (Low-Density Lipoprotein)

47 mg/mL
In range

Triglycerides

158 mg/mL
Above range

A bronchodilator medication that helps to improve breathing by relaxing and opening the airways in the lungs.
A steroid that can be used to reduce inflammation in the airways. This can help with breathing difficulties and coughing.
A macrolide-type antibiotic used to treat a variety of bacterial infections. It works by stopping the growth of bacteria.
“Dr. Puopolo is a very knowledgeable doctor with vast experience in different medical fields. I feel I am in good hands.”
Verified Patient

“Great experience!! Never have done online telehealth before but for sure will again :)”
Verified Patient

“Dr. Culpepper was amazing. He explained things to me that I didn’t understand.”
Verified Patient

“Dr. Sehgal was amazing! Super helpful. She was answering my questions before I even asked. Very happy I picked her.”
Verified Patient

"The appointment went great. It was quick and easy, and the doctor was right on top of things!"
Verified Patient

Reviews shown are from verified LifeMD patients across various services. Photos are for illustrative purposes only.
Bronchitis can cause coughing, wheezing, chest tightness, shortness of breath, fatigue, body aches, and a mild fever. Acute bronchitis may also cause a sore throat, nasal congestion, and runny nose. Chronic bronchitis is often caused by smoking or exposure to irritants and is characterized by a persistent cough that produces mucus.
If you’re experiencing any of these symptoms, be sure to consult with a healthcare provider for an accurate diagnosis and proper treatment.
Yes, bronchitis can be contagious. When it’s caused by a virus or bacteria, it can be spread from person to person through respiratory droplets when an infected person coughs or sneezes. Therefore, if you have bronchitis, it’s important to take precautions such as: covering your mouth and nose when coughing or sneezing, washing your hands frequently, and avoiding close contact with others to prevent the spread of infection.
Drinking fluids is important when you have bronchitis because it helps to keep your body hydrated and also loosens mucus in the airways, making it easier to cough up. Dehydration can make mucus thicker and harder to expel, which can worsen symptoms and lead to further respiratory complications. Lots of fluids — particularly water and warm liquids such as tea or broth — can also help soothe sore throats and alleviate coughing.
Bronchitis is the inflammation of the bronchial tubes. It’s often caused by a virus and has symptoms such as coughing, chest discomfort, and shortness of breath. Pneumonia is caused by bacteria, viruses, or fungi. It’s more severe and affects the air sacs in the lungs. Symptoms of pneumonia include fever, coughing with phlegm, chest pain, and difficulty breathing. Pneumonia can be life-threatening, especially for people with weakened immune systems and/or certain underlying health conditions.
Bronchitis typically resolves on its own in a few weeks with proper treatment. However, in some cases, bronchitis can progress to pneumonia. This is more common in people with weakened immune systems or underlying lung conditions, such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
If you’re experiencing symptoms of bronchitis, it's important to consult with a healthcare provider for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. If your symptoms worsen or you develop new symptoms such as chest pain or difficulty breathing, be sure to seek medical attention right away to rule out the possibility of pneumonia.
Bronchitis is typically not life-threatening and usually resolves in a few weeks with proper treatment. In rare cases, however, complications can occur and may lead to more severe illness. This is more common in older adults, young children, or those with weakened immune systems. People with certain underlying health conditions may be at increased risk of complications as well.
While not particularly common, COVID-19 can sometimes lead to bronchitis as a complication, particularly in people with pre-existing respiratory conditions or weakened immune systems. Additionally, some of the symptoms of COVID-19, such as coughing and shortness of breath, can mimic those of bronchitis.
If you’re experiencing respiratory symptoms, especially if you’ve been in close contact with someone who has COVID-19, be sure to seek medical attention so you can determine the underlying causes of your symptoms and receive the appropriate treatment.

Family Medicine
4.93 stars 170 reviews


Internal Medicine
4.98 stars 178 reviews


Internal Medicine
4.92 stars 261 reviews


Family Medicine
4.94 stars 178 reviews


Hormone Specialist
4.92 stars 163 reviews
