Schedule
Book a telehealth appointment from wherever you are. No insurance necessary.
Achieve your weight-loss goals with GLP-1 treatments like Wegovy® and Zepbound®, guided by licensed providers every step of the way.
Personalized care for women, with HRT and lifestyle support to ease menopause symptoms and restore balance.
Simple, supportive mental health care on your terms, including access to prescription medication when appropriate.
Care without the wait—connect 24/7 with licensed providers for same-day prescription refills and common concerns like colds, flu, rashes, and more.
Talk to a doctor anytime, anywhere — 24/7 urgent & primary care with a telehealth visit in under one hour.
Get your medication prescribed online and sent same-day to your local pharmacy for pickup.
Save time, money, and the hassle — no in-person visits or insurance required.


Prescription treatments are tailored to your specific condition, ensuring effective relief.

Urgent evaluation is crucial to identify your condition early and prevent complications.
Accurate testing, if needed, can confirm your diagnosis and guide the best course of treatment

Licensed providers can send prescriptions to your local pharmacy within an hour, day or night.
step 1
Book a telehealth appointment from wherever you are. No insurance necessary.

step 2
Meet with a board-certified doctor or nurse practitioner from your mobile device.

step 3
Get a prescription if needed (save up to 90%), and pick it up at your pharmacy.
Hypothyroidism (or underactive thyroid) is a condition in which the thyroid gland does not produce enough thyroid hormones to meet the body's needs. Thyroid hormones are essential for regulating metabolism, energy production, body temperature, and many other important functions.
A diagnosis of hypothyroidism is typically made through blood tests that measure thyroid hormone levels and thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) levels. Treatment usually involves lifelong thyroid hormone replacement therapy to restore and maintain normal thyroid hormone levels in the body.
Get Started Get Started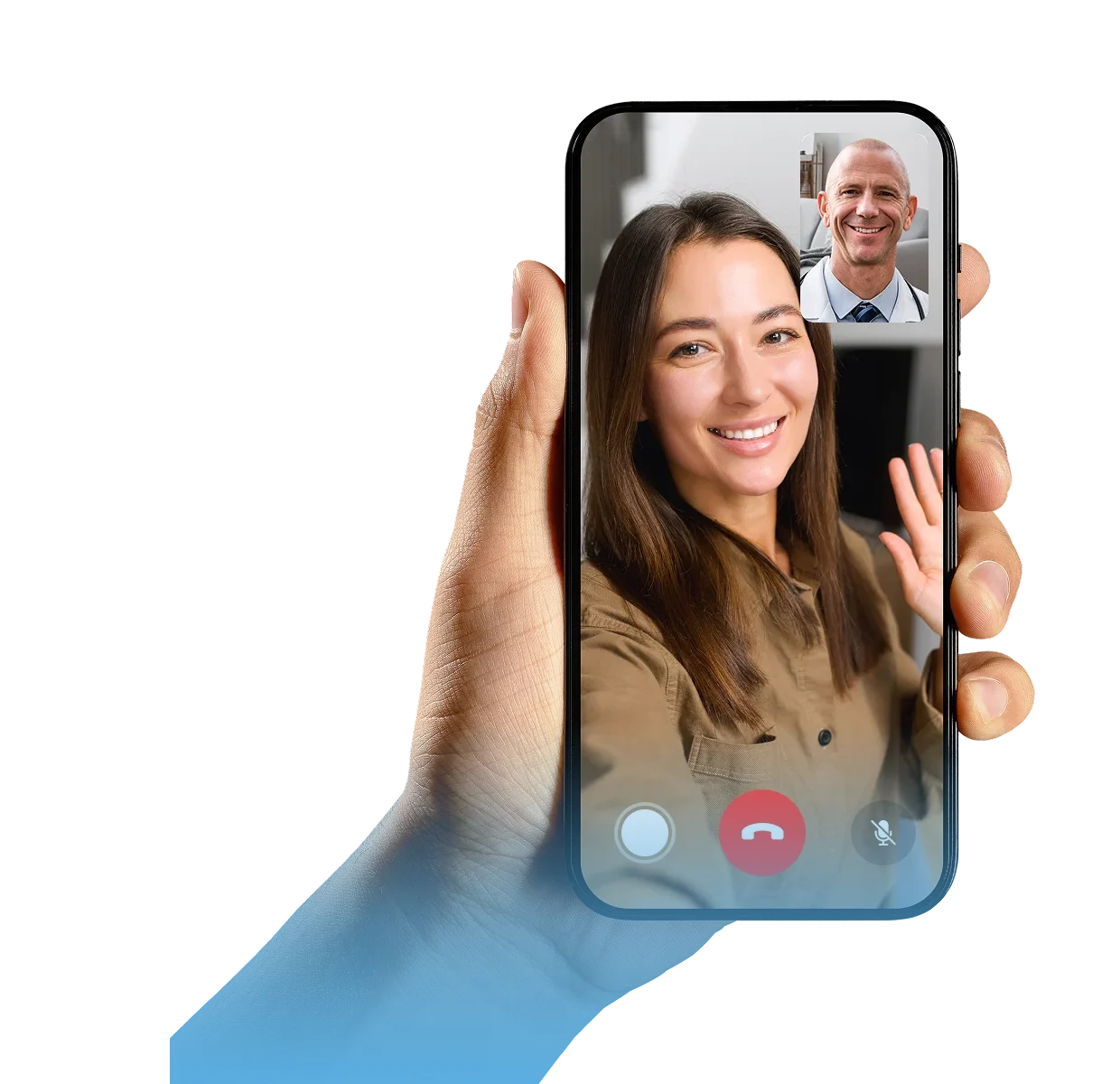
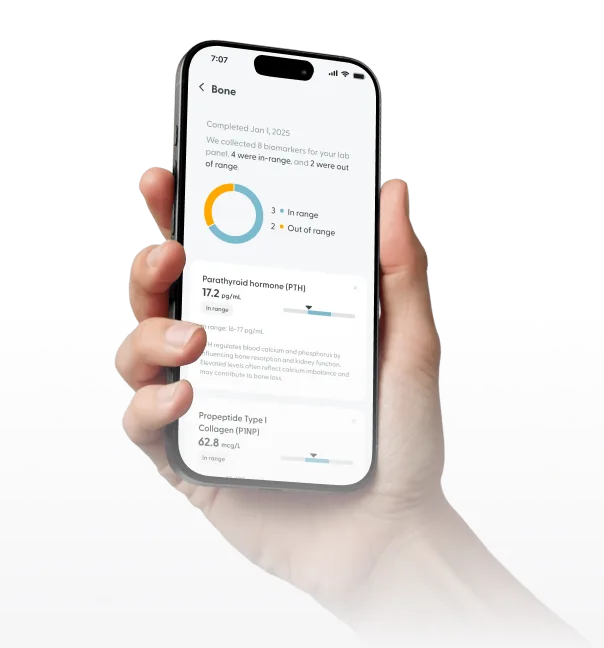
Total Cholesterol

37 mg/mL
In range

LDL (Low-Density Lipoprotein)

47 mg/mL
In range

Triglycerides

158 mg/mL
Above range

A synthetic form of the thyroid hormone thyroxine (T4), and the most commonly prescribed medication for hypothyroidism. Works by replacing or supplementing the deficient thyroid hormone in the body, helping to restore normal thyroid hormone levels.
Contains the synthetic form of the thyroid hormone triiodothyronine (T3). May be used in combination with levothyroxine or as an alternative for some patients who may not adequately respond to levothyroxine alone.
A natural desiccated thyroid hormone medication derived from porcine thyroid glands. It contains both T4 and T3 hormones. Some patients prefer this medication due to its natural origin, but it is less commonly prescribed compared to levothyroxine.
“Dr. Puopolo is a very knowledgeable doctor with vast experience in different medical fields. I feel I am in good hands.”
Verified Patient

“Great experience!! Never have done online telehealth before but for sure will again :)”
Verified Patient

“Dr. Culpepper was amazing. He explained things to me that I didn’t understand.”
Verified Patient

“Dr. Sehgal was amazing! Super helpful. She was answering my questions before I even asked. Very happy I picked her.”
Verified Patient

"The appointment went great. It was quick and easy, and the doctor was right on top of things!"
Verified Patient

Reviews shown are from verified LifeMD patients across various services. Photos are for illustrative purposes only.
There are several signs and symptoms that may indicate hypothyroidism, although it's important to note that not everyone with hypothyroidism will experience all of these symptoms, and some of these symptoms can also be caused by other health conditions. Common signs and symptoms of hypothyroidism may include fatigue, weight gain or difficulty losing weight, cold intolerance, dry skin, brittle nails, constipation, muscle weakness or joint pain, depression, sluggishness or decreased mental sharpness, irregular menstrual periods in women, and increased sensitivity to cold.
If you suspect you may have hypothyroidism, it's important to consult with a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and diagnosis. Diagnosis usually involves a blood test to measure thyroid hormone levels, along with a thorough medical history and physical examination.
Yes, hypothyroidism can disrupt the normal hair growth cycle, leading to hair loss or thinning hair. This is because thyroid hormones play a role in regulating hair follicle function, and when thyroid hormone levels are low, it can result in decreased hair growth, increased shedding, and changes in the texture and thickness of the hair.
Hair loss due to hypothyroidism is usually diffuse and can occur all over the scalp, rather than in specific patches, and it may be one of the noticeable symptoms of an underactive thyroid. Proper diagnosis and management of hypothyroidism, including thyroid hormone replacement therapy, can help alleviate hair loss associated with this condition.
Yes, hypothyroidism, a condition where the thyroid gland does not produce enough thyroid hormones, can cause weight gain. Thyroid hormones play a key role in regulating the body's metabolism, including the rate at which it burns calories. When thyroid hormone levels are low, as in hypothyroidism, the body's metabolic rate may slow down, leading to decreased calorie burning and potential weight gain. Additionally, hypothyroidism can cause other symptoms such as fatigue, muscle weakness, and fluid retention, which can contribute to weight gain.
It's important to note that weight gain in hypothyroidism is typically modest and not solely responsible for significant weight changes. Proper diagnosis and management of hypothyroidism, including medication to replace the deficient thyroid hormones, can help regulate metabolism and manage weight gain associated with this condition.
Yes, hypothyroidism can sometimes cause symptoms of anxiety, including nervousness, irritability, and restlessness, due to the impact of low thyroid hormone levels on the body's overall metabolism and hormonal balance.
Yes, hypothyroidism can have a genetic component, as certain genetic factors can increase the risk of developing the condition. However, genetics alone don’t necessarily determine whether a person will develop hypothyroidism — as other factors such as environmental, hormonal, and autoimmune factors can also play a role. It's important to work with a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and management if there is a family history of hypothyroidism or concerns about genetic predisposition.
Hypothyroidism is typically a chronic condition that requires lifelong thyroid hormone replacement therapy for management, but with proper treatment, most people with hypothyroidism can effectively manage their symptoms and lead healthy lives.
Subclinical hypothyroidism is a condition where TSH levels are slightly elevated while thyroid hormone levels are within the normal range. It may not always cause noticeable symptoms but can increase the risk of overt hypothyroidism. Treatment is considered on an individual basis, and may involve thyroid hormone replacement therapy if deemed necessary. Regular monitoring is very important.

Family Medicine
4.93 stars 170 reviews


Internal Medicine
4.98 stars 178 reviews


Internal Medicine
4.92 stars 261 reviews


Family Medicine
4.94 stars 178 reviews


Hormone Specialist
4.92 stars 163 reviews
