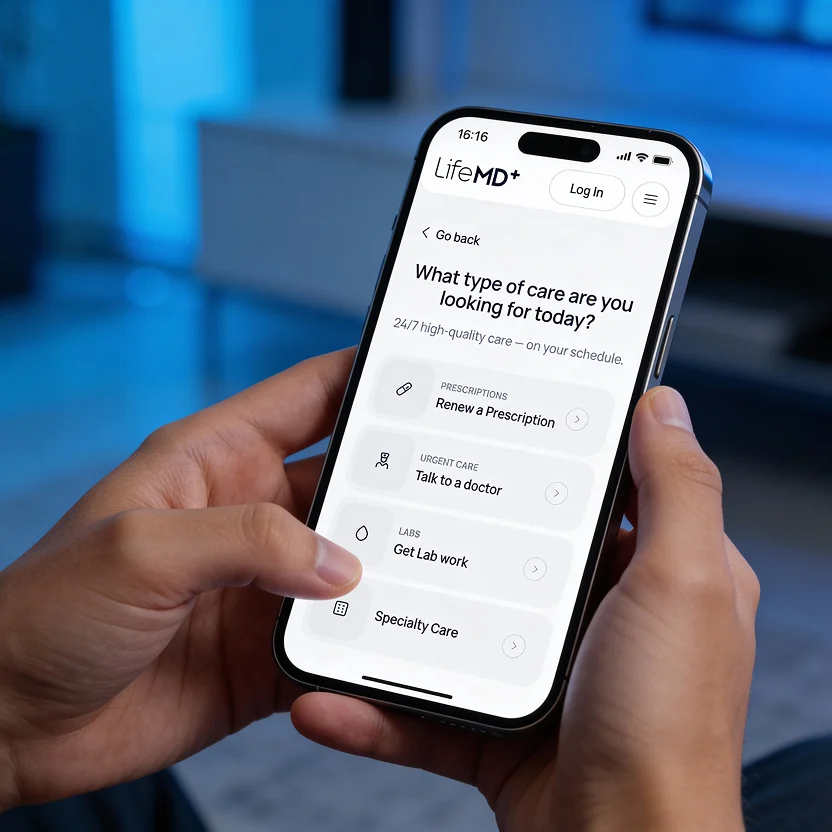
Schedule
Book a telehealth appointment from wherever you are. No insurance necessary.
Achieve your weight-loss goals with GLP-1 treatments like Wegovy® and Zepbound®, guided by licensed providers every step of the way.
Personalized care for women, with HRT and lifestyle support to ease menopause symptoms and restore balance.
Simple, supportive mental health care on your terms, including access to prescription medication when appropriate.
Connect with board-certified cardiologists to help manage blood pressure, cholesterol, and long-term cardiovascular risk — from the comfort of home.
Care without the wait—connect 24/7 with licensed providers for same-day prescription refills and common concerns like colds, flu, rashes, and more.
Talk to a doctor anytime, anywhere — 24/7 urgent & primary care with a telehealth visit in under one hour.
Get your medication prescribed online and sent same-day to your local pharmacy for pickup.
Save time, money, and the hassle — no in-person visits or insurance required.


Prescription treatments are tailored to your specific condition, ensuring effective relief.

Urgent evaluation is crucial to identify your condition early and prevent complications.
Accurate testing, if needed, can confirm your diagnosis and guide the best course of treatment

Licensed providers can send prescriptions to your local pharmacy within an hour, day or night.
step 1
Book a telehealth appointment from wherever you are. No insurance necessary.

step 2
Meet with a board-certified doctor or nurse practitioner from your mobile device.

step 3
Get a prescription if needed (save up to 90%), and pick it up at your pharmacy.
Gout is a type of inflammatory arthritis that occurs when high levels of uric acid accumulate in the blood, leading to the formation of urate crystals in the joints and surrounding tissues. This results in sudden and severe pain, swelling, redness, and warmth in the affected joint.
Gout is common in the big toe, but can also occur in the ankles, knees, hands, and wrists. Gout is commonly managed with medications, lifestyle changes, and dietary modifications to reduce uric acid levels and prevent future attacks.
Get Started Get Started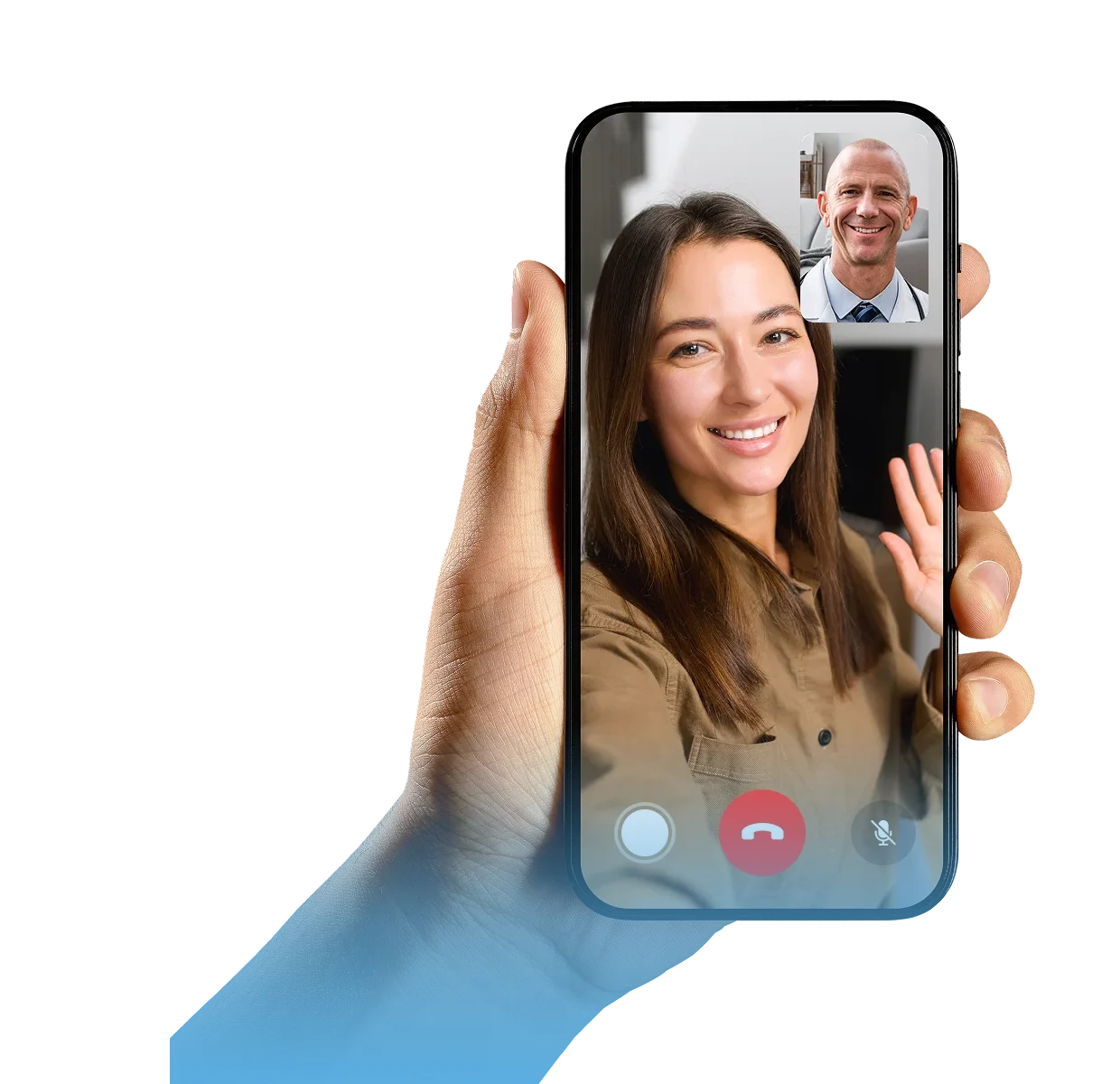
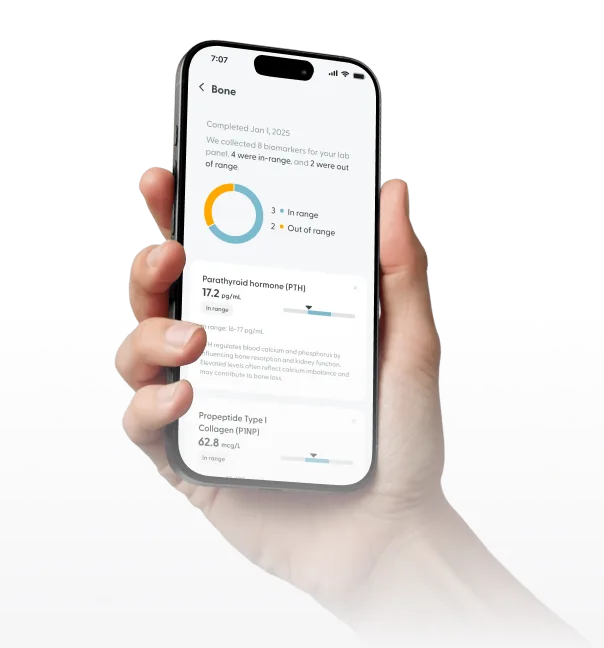
Total Cholesterol

37 mg/mL
In range

LDL (Low-Density Lipoprotein)

47 mg/mL
In range

Triglycerides

158 mg/mL
Above range

An anti-inflammatory medication that can help reduce the pain and inflammation associated with acute gout attacks.
Works by suppressing the immune system's response to inflammation, which can help alleviate the symptoms of a gout attack.
Works by reducing the production of uric acid in the body, making it useful for preventing gout attacks and managing certain other conditions associated with high uric acid levels.
“Dr. Puopolo is a very knowledgeable doctor with vast experience in different medical fields. I feel I am in good hands.”
Verified Patient

“Great experience!! Never have done online telehealth before but for sure will again :)”
Verified Patient

“Dr. Culpepper was amazing. He explained things to me that I didn’t understand.”
Verified Patient

“Dr. Sehgal was amazing! Super helpful. She was answering my questions before I even asked. Very happy I picked her.”
Verified Patient

"The appointment went great. It was quick and easy, and the doctor was right on top of things!"
Verified Patient

Reviews shown are from verified LifeMD patients across various services. Photos are for illustrative purposes only.
Gout causes sudden and severe pain, swelling, and tenderness in the affected joint. The pain is often described as a burning or stabbing sensation that can be excruciating. The affected joint may also feel hot to the touch, and the skin over the joint may appear red and shiny. People with gout may also find it difficult to move the affected joint.
Gout attacks can come on suddenly and usually occur at night, lasting several hours to a few days. Some people with gout may experience chronic pain and joint damage if the condition is not managed properly.
The first sign of gout is sudden, intense pain, tenderness, redness, and swelling in the affected joint, often within the first 12-24 hours of the gout attack. Other symptoms may include fever or fatigue.
Gout flare-ups occur as a result of the buildup of uric acid crystals in the joints, leading to inflammation and pain. Uric acid is a waste product normally eliminated through urine, but excess amounts can form crystals in the joints. Gout flare-ups can be triggered by factors such as eating a lot of high-purine foods, not drinking enough water and healthy liquids, being exposed to prolonged stress, injuring a joint, and taking certain medications. Managing triggers can help prevent flare-ups.
Certain foods are known to trigger gout attacks by increasing the levels of uric acid in the body. These foods include high-purine animal products such as red meat, organ meats (e.g. liver, kidneys), seafood (e.g. anchovies, sardines, mussels), and some types of game meats. Alcohol, particularly beer, is also a known trigger for gout attacks, as it increases uric acid production and impairs its excretion from the body.
Other foods and beverages that may contribute to gout include sugary drinks, fructose, and high-fat dairy products. People with gout (or who are prone to gout attacks) are advised to limit or avoid these foods and to maintain a healthy weight, as obesity can also increase the risk of a gout flare-up.
Yes, gout is a type of arthritis caused by the buildup of uric acid crystals in the joints. It triggers an immune response that leads to joint inflammation, pain, and swelling. Gout can cause joint damage and other health problems if left untreated. Seeking treatment is important to manage symptoms and prevent long-term complications.
Yes, genetic factors can play a role in the development of gout, particularly in the way that the body processes and eliminates uric acid. People with a family history of gout are more likely to develop the condition themselves, and studies have identified specific genetic mutations that increase the risk of gout. However, genetics isn’t the only factor that contributes to gout. Lifestyle factors such as diet and alcohol consumption also play a key role. Therefore, while genetics may increase the risk of developing gout, it’s not a guarantee and can be managed through lifestyle changes and medication.
To alleviate gout pain at night, apply an ice pack or elevate the affected joint. Over-the-counter pain relievers may help, but should be used under the guidance of a healthcare professional. Drinking plenty of fluids, avoiding alcohol and sugary drinks, and maintaining a healthy weight can also reduce the frequency and severity of gout attacks. A low-purine diet and avoiding trigger foods can also help prevent gout attacks. Be sure to consult with a healthcare professional if gout pain is severe or persistent.

Family Medicine
4.93 stars 170 reviews


Internal Medicine
4.98 stars 178 reviews


Internal Medicine
4.92 stars 261 reviews


Family Medicine
4.94 stars 178 reviews


Hormone Specialist
4.92 stars 163 reviews
