Schedule
Book a telehealth appointment from wherever you are. No insurance necessary.
Achieve your weight-loss goals with GLP-1 treatments like Wegovy® and Zepbound®, guided by licensed providers every step of the way.
Personalized care for women, with HRT and lifestyle support to ease menopause symptoms and restore balance.
Simple, supportive mental health care on your terms, including access to prescription medication when appropriate.
Care without the wait—connect 24/7 with licensed providers for same-day prescription refills and common concerns like colds, flu, rashes, and more.
Talk to a doctor anytime, anywhere — 24/7 urgent & primary care with a telehealth visit in under one hour.
Get your medication prescribed online and sent same-day to your local pharmacy for pickup.
Save time, money, and the hassle — no in-person visits or insurance required.


Prescription treatments are tailored to your specific condition, ensuring effective relief.

Urgent evaluation is crucial to identify your condition early and prevent complications.
Accurate testing, if needed, can confirm your diagnosis and guide the best course of treatment

Licensed providers can send prescriptions to your local pharmacy within an hour, day or night.
step 1
Book a telehealth appointment from wherever you are. No insurance necessary.

step 2
Meet with a board-certified doctor or nurse practitioner from your mobile device.

step 3
Get a prescription if needed (save up to 90%), and pick it up at your pharmacy.
Back pain is a common condition that affects people of all ages and can range from mild discomfort to debilitating pain. It can result from injury, muscle strain, poor posture, or underlying health issues — such as arthritis, herniated discs, or in rare cases, cancer.
While back pain can feel frustrating and limiting, various treatments and self-care strategies can help manage and alleviate symptoms. A licensed healthcare provider can help you understand what's causing your back pain so you can find relief.
Get Started Get Started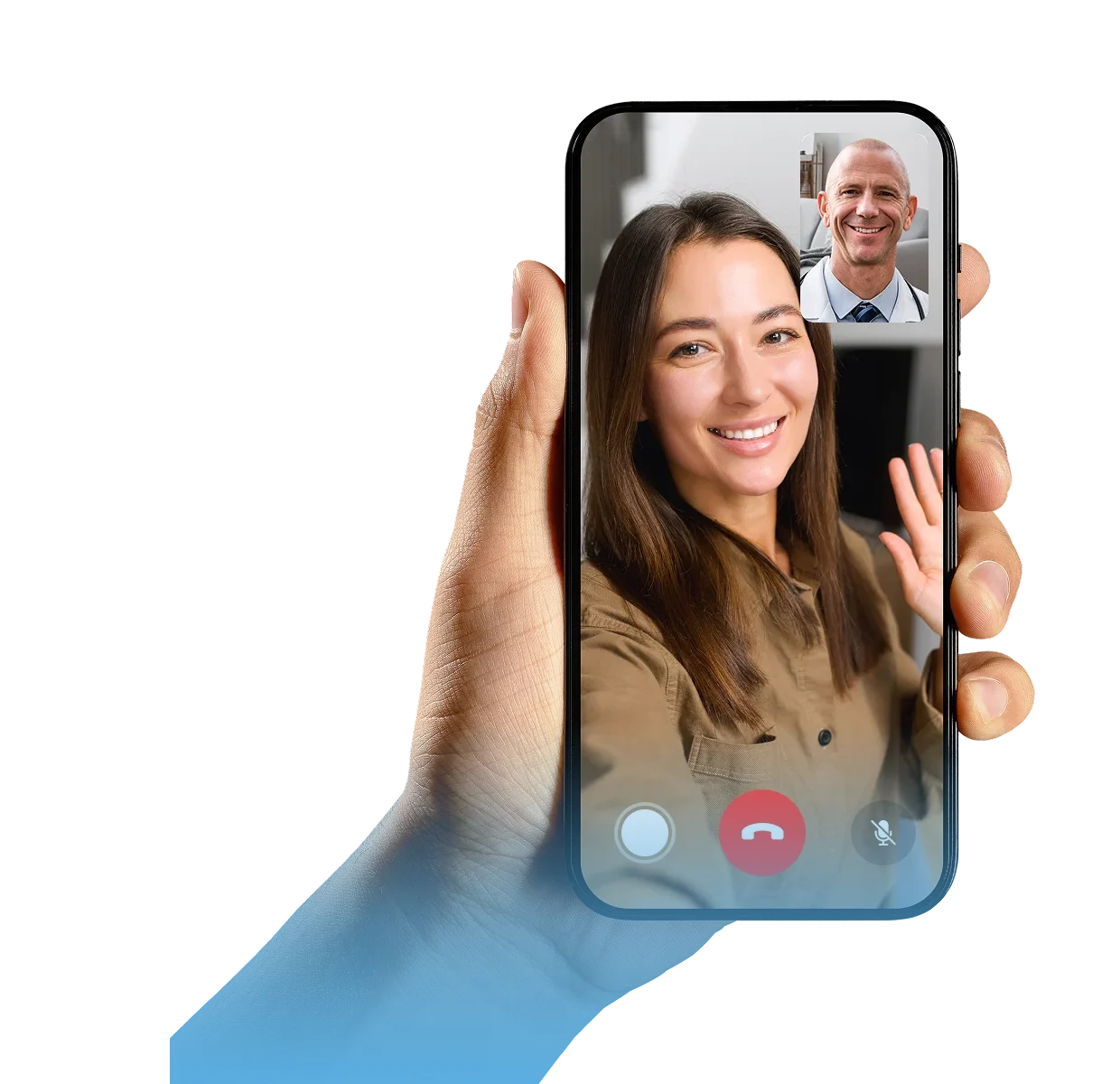
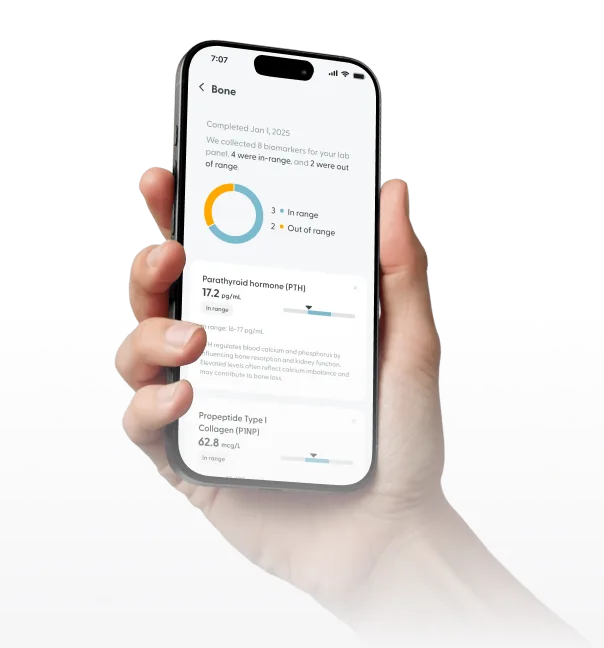
Total Cholesterol

37 mg/mL
In range

LDL (Low-Density Lipoprotein)

47 mg/mL
In range

Triglycerides

158 mg/mL
Above range

A prescription nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) that helps reduce inflammation, pain, and stiffness associated with back pain. Celecoxib is a COX-2 inhibitor, which may cause fewer gastrointestinal side effects than traditional NSAIDs.
Prescription medications such as cyclobenzaprine (Flexeril) or tizanidine (Zanaflex) may be prescribed for short-term relief of muscle spasms and back pain.
A corticosteroid medication that may be prescribed for short-term use in reducing inflammation and relieving acute back pain.
“Dr. Puopolo is a very knowledgeable doctor with vast experience in different medical fields. I feel I am in good hands.”
Verified Patient

“Great experience!! Never have done online telehealth before but for sure will again :)”
Verified Patient

“Dr. Culpepper was amazing. He explained things to me that I didn’t understand.”
Verified Patient

“Dr. Sehgal was amazing! Super helpful. She was answering my questions before I even asked. Very happy I picked her.”
Verified Patient

"The appointment went great. It was quick and easy, and the doctor was right on top of things!"
Verified Patient

Reviews shown are from verified LifeMD patients across various services. Photos are for illustrative purposes only.
Back pain can be caused by a variety of factors, including muscle or ligament strains, poor posture, herniated discs, spinal abnormalities, osteoarthritis, or injuries. In some cases, back pain may be a sign of an underlying condition such as cancer.
Consult a healthcare professional if your back pain is severe, persistent, or accompanied by other symptoms, such as fever, unexplained weight loss, or numbness and tingling in the legs. It’s also important to seek medical attention if the pain results from an injury or trauma, or if it’s affecting your daily activities and quality of life.
Yes, regular exercise can help alleviate and prevent back pain. Strengthening exercises for the core and back muscles, as well as maintaining flexibility, can support the spine and reduce the risk of injury. Low-impact activities such as walking, swimming, or yoga can also be beneficial for back pain sufferers.
Poor posture can contribute to back pain by placing excessive strain on the muscles and ligaments that support the spine. Maintaining good posture, especially while sitting or standing for extended periods, can help prevent and alleviate back pain.
To help prevent back pain, be sure to maintain a healthy weight, practice good posture, engage in regular exercise with a focus on core and back muscle strength, use proper lifting techniques, and ensure your workstation is ergonomically designed to support your spine.
While most cases of back pain are not caused by serious conditions, it can sometimes be a symptom of an underlying health issue, such as a herniated disc, spinal stenosis, osteoarthritis, or even cancer. Persistent or severe back pain, especially when accompanied by other symptoms, should be evaluated by a healthcare professional to determine the cause and appropriate treatment.

Family Medicine
4.93 stars 170 reviews


Internal Medicine
4.98 stars 178 reviews


Internal Medicine
4.92 stars 261 reviews


Family Medicine
4.94 stars 178 reviews


Hormone Specialist
4.92 stars 163 reviews
