Schedule
Book a telehealth appointment from wherever you are. No insurance necessary.
Achieve your weight-loss goals with GLP-1 treatments like Wegovy® and Zepbound®, guided by licensed providers every step of the way.
Personalized care for women, with HRT and lifestyle support to ease menopause symptoms and restore balance.
Simple, supportive mental health care on your terms, including access to prescription medication when appropriate.
Connect with board-certified cardiologists to help manage blood pressure, cholesterol, and long-term cardiovascular risk — from the comfort of home.
Care without the wait—connect 24/7 with licensed providers for same-day prescription refills and common concerns like colds, flu, rashes, and more.
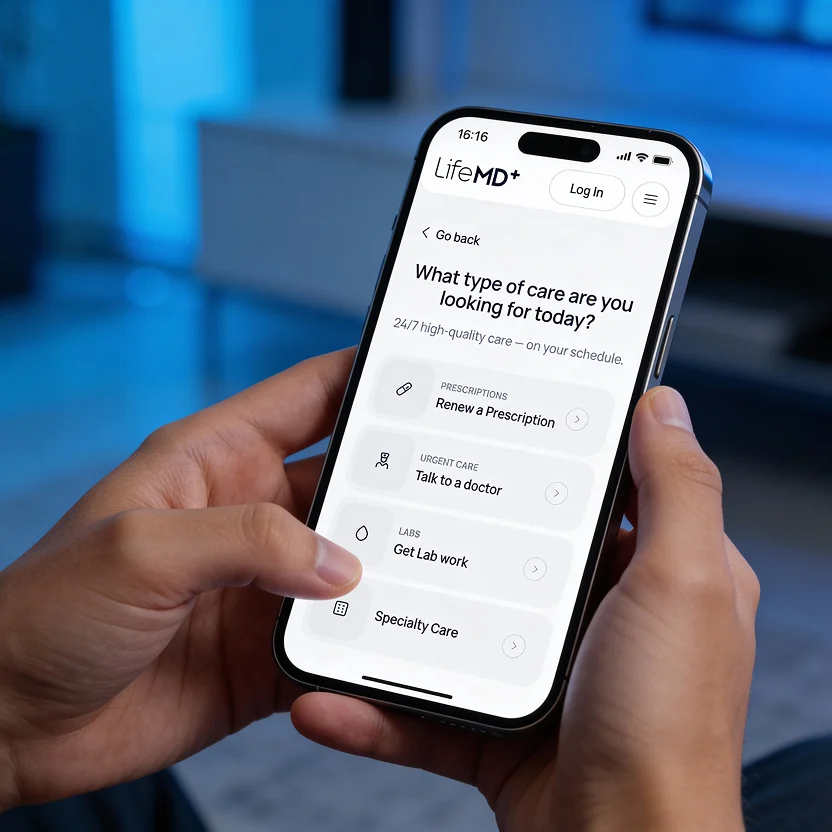
Talk to a doctor anytime, anywhere — 24/7 urgent & primary care with a telehealth visit in under one hour.
Get lab tests and your medication prescribed online and sent same-day to your local pharmacy for pickup.
Save time, money, and the hassle—no in-person visits or insurance required.


Prescription treatments are tailored to your specific condition, ensuring effective relief.

Urgent evaluation is crucial to identify your condition early and prevent complications.
Accurate testing, if needed, can confirm your diagnosis and guide the best course of treatment

Licensed providers can send prescriptions to your local pharmacy within an hour, day or night.
step 1
Book a telehealth appointment from wherever you are. No insurance necessary.

step 2
Meet with a board-certified doctor or nurse practitioner from your mobile device.

step 3
Get a prescription if needed (save up to 90%), and pick it up at your pharmacy.
Chlamydia is a common sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by the bacterium Chlamydia trachomatis. It can infect both men and women and is transmitted through sexual contact.
Chlamydia often has no symptoms, making it difficult to detect and increasing the risk of complications if left untreated. However, it can be easily diagnosed with a simple test and effectively treated with antibiotics.
Get Started Get Started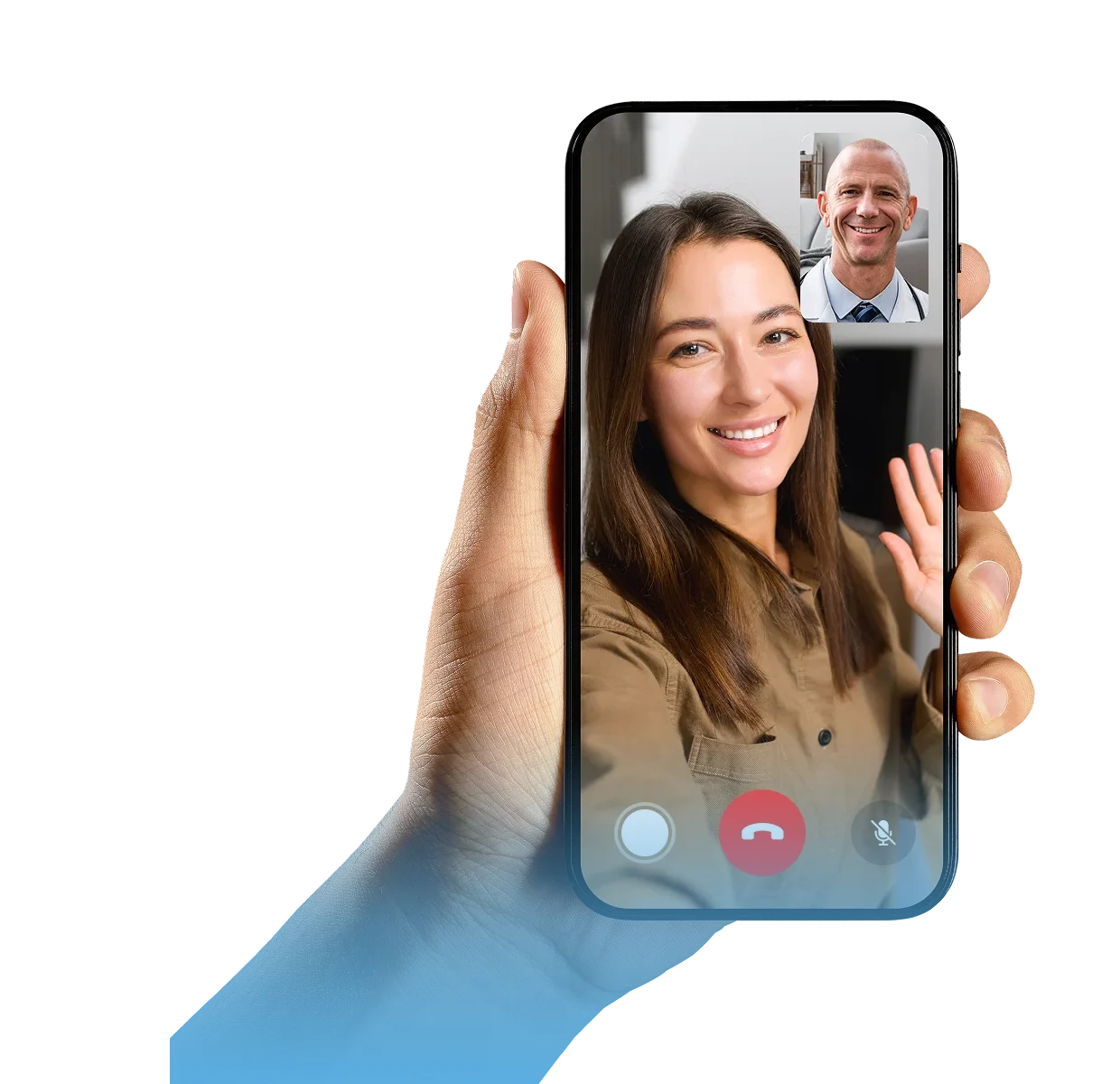
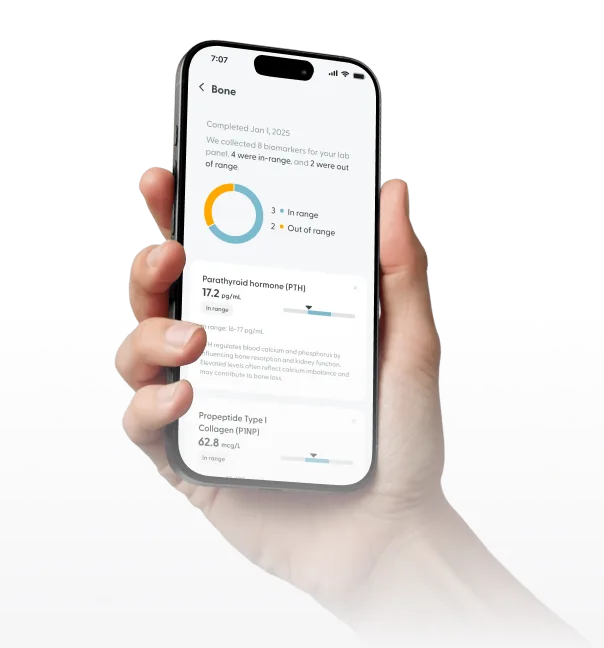
Total Cholesterol

37 mg/mL
In range

LDL (Low-Density Lipoprotein)

47 mg/mL
In range

Triglycerides

158 mg/mL
Above range

A macrolide antibiotic that is taken as a single dose to treat chlamydia. It works by stopping the growth of bacteria and is effective in clearing the infection in most cases.
A tetracycline antibiotic that works by inhibiting bacterial protein synthesis and is effective in clearing a chlamydia infection.
Aspirin, ibuprofen, or naproxen can help reduce inflammation and relieve pain while the chlamydia infection clears with the help of antibiotics.
“Dr. Puopolo is a very knowledgeable doctor with vast experience in different medical fields. I feel I am in good hands.”
Verified Patient

“Great experience!! Never have done online telehealth before but for sure will again :)”
Verified Patient

“Dr. Culpepper was amazing. He explained things to me that I didn’t understand.”
Verified Patient

“Dr. Sehgal was amazing! Super helpful. She was answering my questions before I even asked. Very happy I picked her.”
Verified Patient

"The appointment went great. It was quick and easy, and the doctor was right on top of things!"
Verified Patient

Reviews shown are from verified LifeMD patients across various services. Photos are for illustrative purposes only.
Many people with chlamydia have no symptoms. When symptoms do occur, they may include: abnormal vaginal discharge or pain during urination in women; discharge from the penis, pain during urination, or swollen testicles in men.
Chlamydia often presents with no symptoms or very mild ones, making it difficult to detect without proper testing. However, when symptoms do occur, they may include: For women: * Abnormal vaginal discharge * Painful urination * Pain during sexual intercourse * Lower abdominal pain * Bleeding between periods or after sex For men: * Discharge from the penis * Painful urination * Swelling or pain in the testicles If you’re experiencing any of these symptoms or suspect you may have been exposed to chlamydia, be sure to seek prompt medical attention, as untreated infections can lead to more severe complications.
Chlamydia is mainly spread through sexual activities involving the exchange of bodily fluids with an infected partner, such as vaginal, anal, or oral sex. Although it’s possible to get chlamydia from kissing, the chances of transmission through this mode of contact are relatively low.
The only way to know for sure if you have chlamydia is to get tested by a healthcare professional. Chlamydia is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by the bacterium Chlamydia trachomatis, and it can often present with no symptoms. Testing involves a simple urine test or swab of the genital area, which can detect the presence of the bacteria.
If you suspect you have chlamydia or have had unprotected sex, it’s important to get tested and treated promptly to prevent the spread of the infection and avoid potential long-term health complications.
Chlamydia can be effectively treated with antibiotics prescribed by a licensed health provider. The most common medications used to treat chlamydia are azithromycin (Zithromax) and doxycycline (Vibramycin).
It’s extremely important to complete the full course of antibiotics, even if symptoms improve before the medication is finished. This helps ensure the infection is fully cleared. Additionally, it's essential to abstain from sexual activity until the treatment is complete and the infection has resolved.
If left untreated, chlamydia can cause serious health problems. In women, it can lead to pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), which may result in infertility, chronic pelvic pain, or ectopic pregnancy. In men, chlamydia can cause epididymitis, which may lead to infertility if not treated. Additionally, untreated chlamydia can increase the risk of acquiring or transmitting HIV.
The duration of a chlamydia infection can vary depending on when it’s detected and treated. With prompt and proper treatment using prescribed antibiotics, such as azithromycin (Zithromax) and doxycycline (Vibramycin), most chlamydia infections clear within one to two weeks. It's very important to complete the full course of antibiotics and abstain from sexual activity during the treatment period to ensure the infection is fully cleared and to prevent reinfection or transmission to others.
While chlamydia can be effectively treated and cured, it’s possible to become reinfected if exposed to the bacterium again. Practicing safe sex and getting tested regularly can help reduce the risk of recurrent infections.
It’s strongly advised to refrain from sex while infected with chlamydia, as it can be easily transmitted to your partner through unprotected sexual contact. Once the infection has been fully treated and cleared, and your healthcare professional has given you the green light, you can resume sexual activity. Make sure to inform any sexual partner(s) about your infection so they can also seek testing and treatment if necessary.

Family Medicine
4.93 stars 170 reviews


Internal Medicine
4.98 stars 178 reviews


Internal Medicine
4.92 stars 261 reviews


Family Medicine
4.94 stars 178 reviews


Hormone Specialist
4.92 stars 163 reviews
