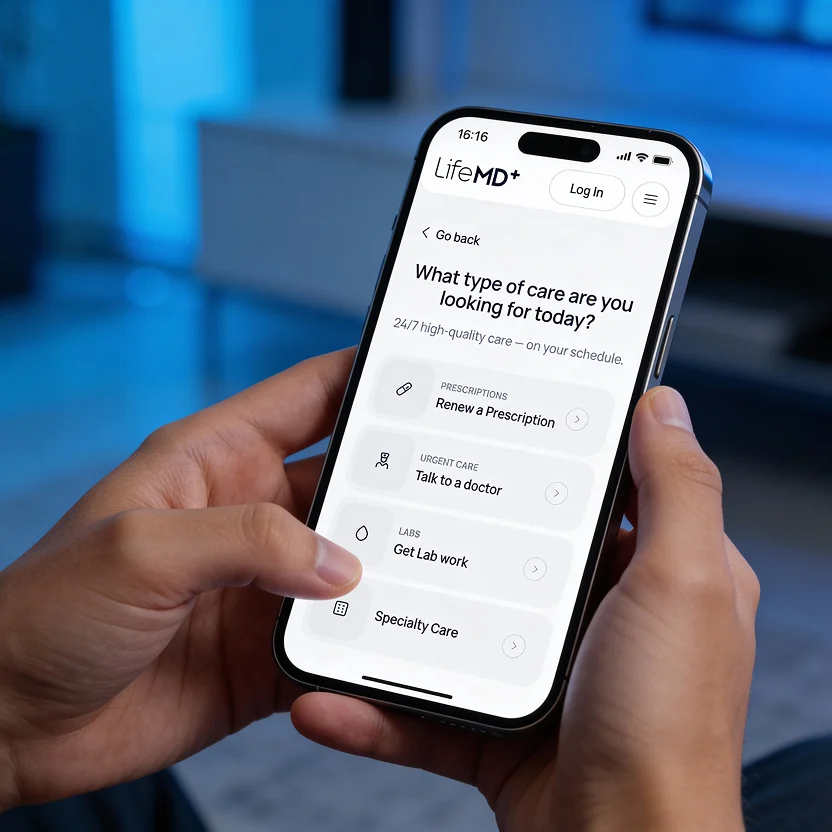
Schedule
Book a telehealth appointment from wherever you are. No insurance necessary.
Achieve your weight-loss goals with GLP-1 treatments like Wegovy® and Zepbound®, guided by licensed providers every step of the way.
Personalized care for women, with HRT and lifestyle support to ease menopause symptoms and restore balance.
Simple, supportive mental health care on your terms, including access to prescription medication when appropriate.
Connect with board-certified cardiologists to help manage blood pressure, cholesterol, and long-term cardiovascular risk — from the comfort of home.
Care without the wait—connect 24/7 with licensed providers for same-day prescription refills and common concerns like colds, flu, rashes, and more.
Talk to a doctor anytime, anywhere — 24/7 urgent & primary care with a telehealth visit in under one hour.
Get your medication prescribed online and sent same-day to your local pharmacy for pickup.
Save time, money, and the hassle — no in-person visits or insurance required.


Prescription treatments are tailored to your specific condition, ensuring effective relief.

Urgent evaluation is crucial to identify your condition early and prevent complications.
Accurate testing, if needed, can confirm your diagnosis and guide the best course of treatment

Licensed providers can send prescriptions to your local pharmacy within an hour, day or night.
step 1
Book a telehealth appointment from wherever you are. No insurance necessary.

step 2
Meet with a board-certified doctor or nurse practitioner from your mobile device.

step 3
Get a prescription if needed (save up to 90%), and pick it up at your pharmacy.
Hemorrhoids are swollen veins in the lower rectum and anus that can cause pain, itching, and bleeding during bowel movements. They can develop due to increased pressure on the veins in the pelvic and rectal area, often resulting from constipation, pregnancy, or straining during bowel movements.
Hemorrhoids can be internal (inside the rectum) or external (under the skin around the anus). Treatment options vary depending on the severity of the hemorrhoids and the associated symptoms.
Get Started Get Started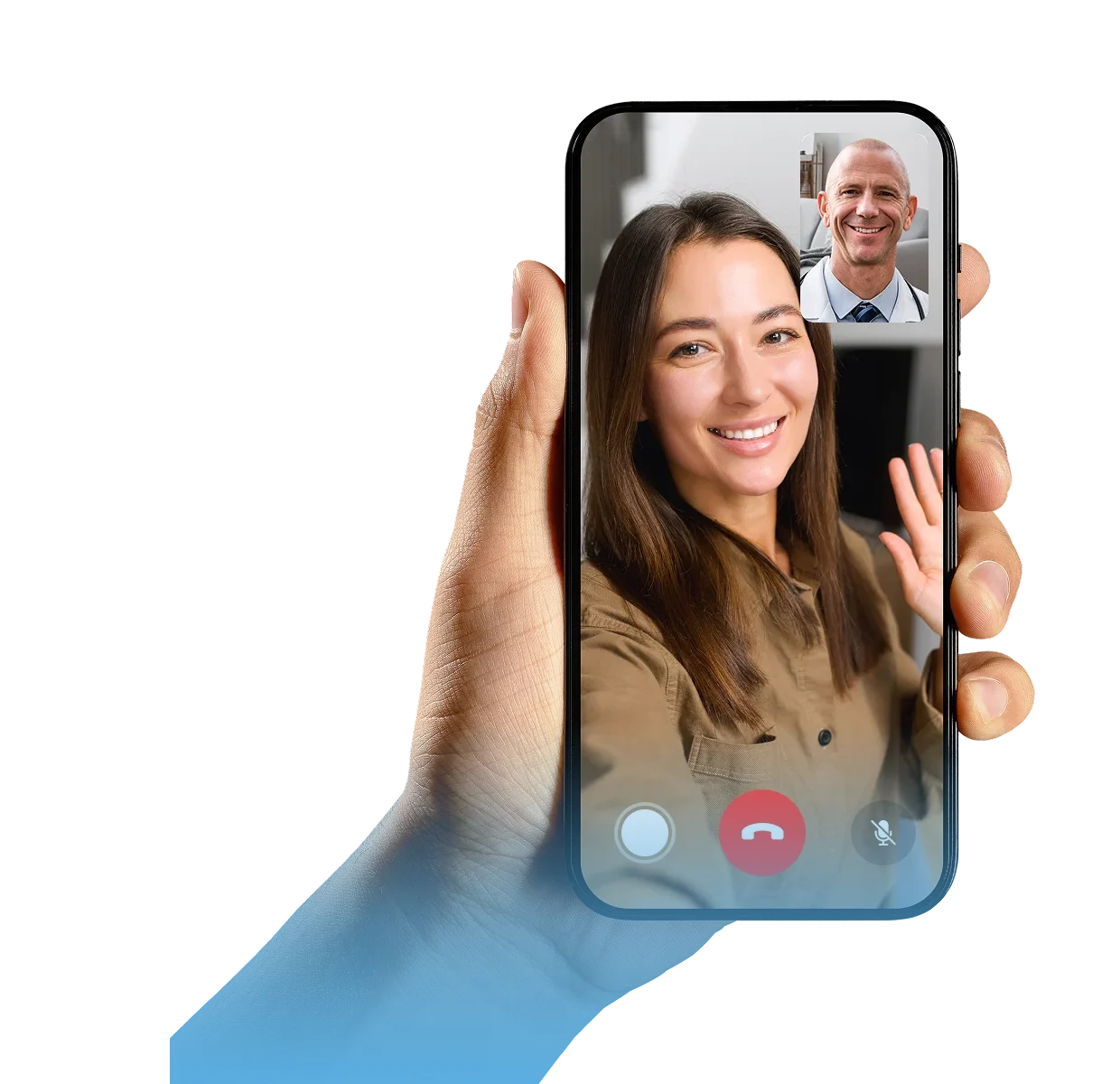
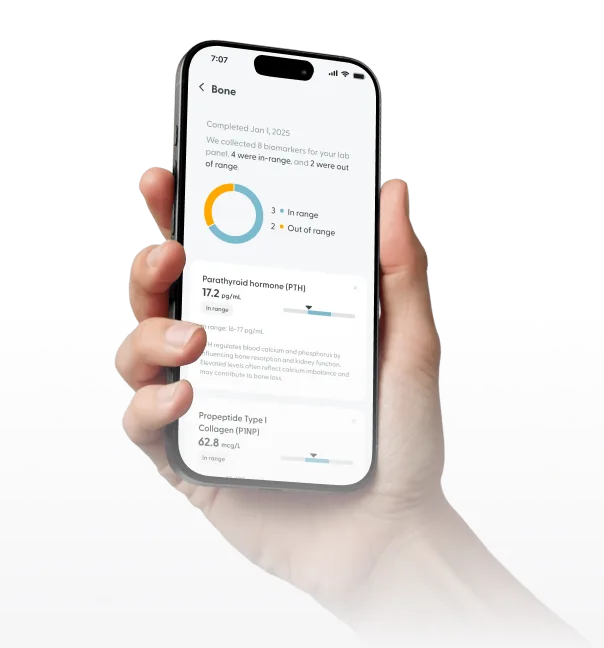
Total Cholesterol

37 mg/mL
In range

LDL (Low-Density Lipoprotein)

47 mg/mL
In range

Triglycerides

158 mg/mL
Above range

Contains hydrocortisone as its active ingredient and is available in various forms such as creams, ointments, and suppositories. Is prescribed to reduce symptoms associated with hemorrhoids such as itching, redness, and inflammation.
Reduces hemorrhoid-related symptoms such as swelling, itching, and inflammation. Ingredients vary by formulation. May contain phenylephrine (works by constricting blood vessels in the affected area) and hydrocortisone (works by suppressing the body's immune response), among other ingredients.
A combination medication that contains cinchocaine hydrochloride and hydrocortisone. It is available in various formulations such as creams, ointments, and suppositories and is used to reduce the pain, itching, swelling, and inflammation associated with hemorrhoids.
“Dr. Puopolo is a very knowledgeable doctor with vast experience in different medical fields. I feel I am in good hands.”
Verified Patient

“Great experience!! Never have done online telehealth before but for sure will again :)”
Verified Patient

“Dr. Culpepper was amazing. He explained things to me that I didn’t understand.”
Verified Patient

“Dr. Sehgal was amazing! Super helpful. She was answering my questions before I even asked. Very happy I picked her.”
Verified Patient

"The appointment went great. It was quick and easy, and the doctor was right on top of things!"
Verified Patient

Reviews shown are from verified LifeMD patients across various services. Photos are for illustrative purposes only.
Hemorrhoids are caused by increased pressure on the veins in the pelvic and rectal area, often resulting from constipation, pregnancy, obesity, or straining during bowel movements. In addition, age (the risk of developing hemorrhoids generally increases with age) and a family history of hemorrhoids play a role as well.
Hemorrhoids typically feel like swollen and inflamed veins in the rectal area. They can cause various sensations, including pain, itching, and discomfort. When external hemorrhoids are present, they may be felt as soft lumps or bumps around the anus. Internal hemorrhoids, on the other hand, may cause a feeling of fullness or pressure in the rectum, along with bleeding during bowel movements. Hemorrhoids can be uncomfortable and may cause pain or discomfort, especially when sitting or during bowel movements.
Hemorrhoids — especially external hemorrhoids — can cause itching or irritation in the rectal area. Scratching the affected area may provide temporary relief but can also further irritate the skin and worsen the condition. It's important to avoid scratching and to seek medical advice for a proper diagnosis and treatment options if you’re experiencing itching or suspect you have hemorrhoids. Your healthcare provider can recommend appropriate measures to help you find relief.
Yes, hemorrhoids can bleed. Bleeding during bowel movements is a common symptom of hemorrhoids, especially internal hemorrhoids. The blood from hemorrhoids is typically bright red and may be noticed on toilet paper, in the toilet bowl, or on the surface of the stool. It’s important to note that rectal bleeding can also be caused by other conditions, so it's extremely important to consult with a healthcare professional if you’re experiencing rectal bleeding.
Mild cases of hemorrhoids may resolve on their own with proper self-care and lifestyle changes, such as increasing fiber intake, drinking plenty of water, and avoiding straining during bowel movements. However, more severe or persistent hemorrhoids may require medical intervention to alleviate symptoms and prevent complications.
To prevent hemorrhoids, focus on maintaining a healthy diet that includes plenty of fiber-rich foods and lots of water. In addition, avoid straining during bowel movements, incorporate regular exercise into your routine, take standing breaks if you tend to sit a lot throughout the day, practice good hygiene, don’t sit too long on the toilet, and use gentle wiping techniques.
A healthcare professional can help with personalized recommendations, especially if you’re prone to hemorrhoids.
You should consider seeing a doctor for hemorrhoids if you’re experiencing persistent or severe symptoms, such as pain that doesn’t let up, bleeding from the rectum, significant swelling, or prolapsed hemorrhoids. A healthcare professional can provide an accurate diagnosis, recommend appropriate treatment options, and help rule out other potential underlying conditions.
Although hemorrhoids are generally not dangerous, they can cause complications if left untreated. Potential complications include anemia due to chronic blood loss, infection, and thrombosed hemorrhoids (which occur when a blood clot forms within an external hemorrhoid, causing severe pain and inflammation).

Family Medicine
4.93 stars 170 reviews


Internal Medicine
4.98 stars 178 reviews


Internal Medicine
4.92 stars 261 reviews


Family Medicine
4.94 stars 178 reviews


Hormone Specialist
4.92 stars 163 reviews
