Schedule
Book a telehealth appointment from wherever you are. No insurance necessary.
Achieve your weight-loss goals with GLP-1 treatments like Wegovy® and Zepbound®, guided by licensed providers every step of the way.
Personalized care for women, with HRT and lifestyle support to ease menopause symptoms and restore balance.
Simple, supportive mental health care on your terms, including access to prescription medication when appropriate.
Connect with board-certified cardiologists to help manage blood pressure, cholesterol, and long-term cardiovascular risk — from the comfort of home.
Care without the wait—connect 24/7 with licensed providers for same-day prescription refills and common concerns like colds, flu, rashes, and more.
Talk to a doctor anytime, anywhere — 24/7 urgent & primary care with a telehealth visit in under one hour.
Get your medication prescribed online and sent same-day to your local pharmacy for pickup.
Save time, money, and the hassle — no in-person visits or insurance required.


Prescription treatments are tailored to your specific condition, ensuring effective relief.

Urgent evaluation is crucial to identify your condition early and prevent complications.
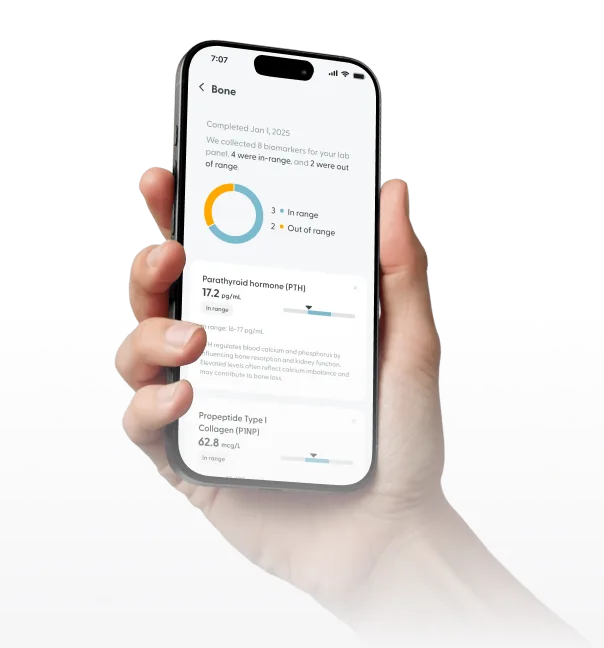
Accurate testing, if needed, can confirm your diagnosis and guide the best course of treatment

Licensed providers can send prescriptions to your local pharmacy within an hour, day or night.
step 1
Book a telehealth appointment from wherever you are. No insurance necessary.

step 2
Meet with a board-certified doctor or nurse practitioner from your mobile device.

step 3
Get a prescription if needed (save up to 90%), and pick it up at your pharmacy.
Asthma is a chronic disease that affects the airways, potentially causing them to become inflamed and narrowed. This can lead to wheezing, coughing, and tightness in the chest. For some people, asthma is a minor nuisance. But for others, it can interfere with daily activities and may lead to a life-threatening asthma attack.
Because asthma often changes over time, it's important to work with a doctor to identify triggers, track symptoms, and adjust treatment as needed.
Get Started Get Started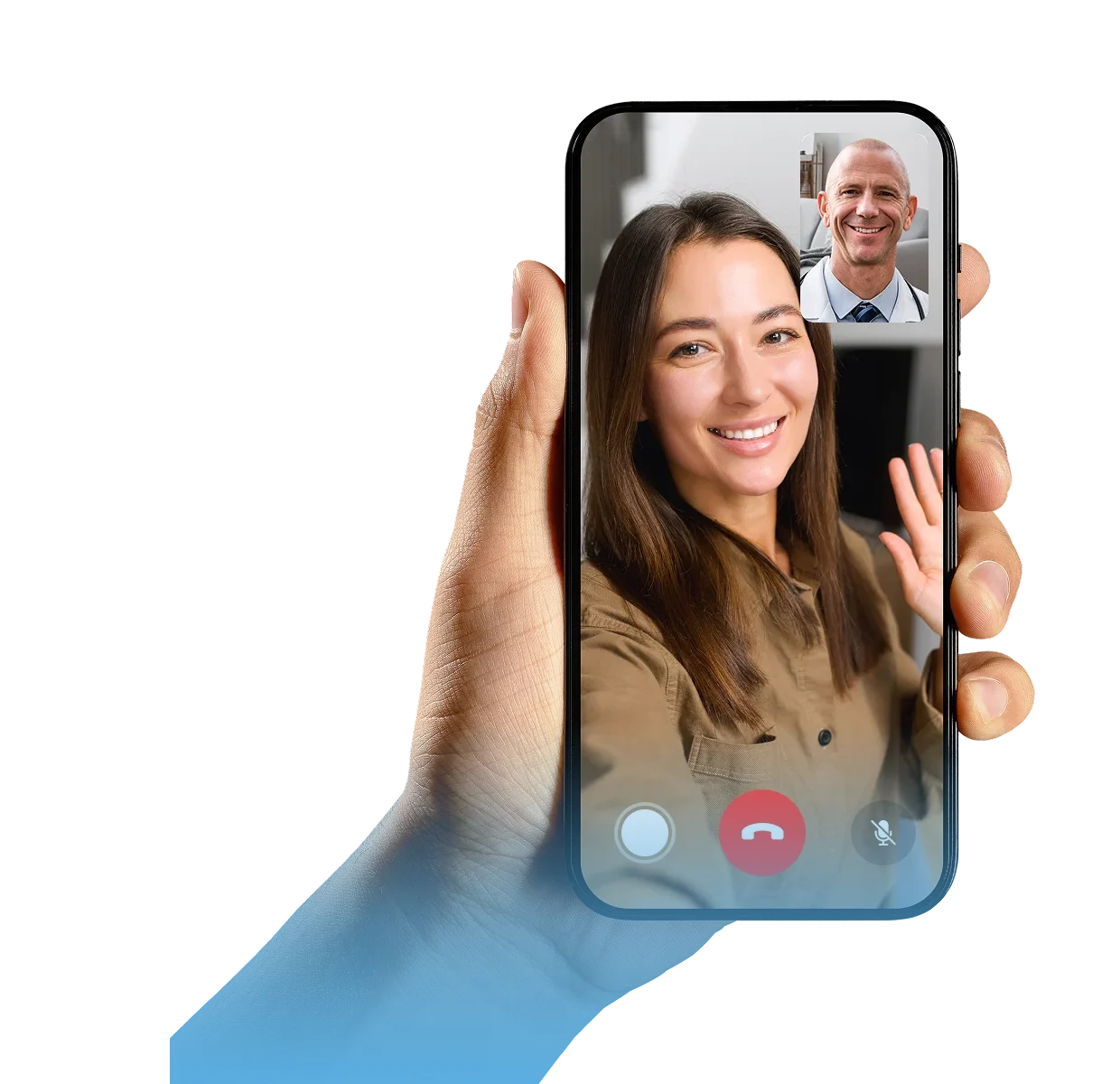
Total Cholesterol

37 mg/mL
In range

LDL (Low-Density Lipoprotein)

47 mg/mL
In range

Triglycerides

158 mg/mL
Above range

A bronchodilator that helps relieve asthma symptoms by opening up the airways.
A combination inhaler that can be used to both reduce inflammation and open up the airways.
Works by blocking the action of leukotrienes, which are substances in the body that can cause inflammation and narrowing of the airways.
“Dr. Puopolo is a very knowledgeable doctor with vast experience in different medical fields. I feel I am in good hands.”
Verified Patient

“Great experience!! Never have done online telehealth before but for sure will again :)”
Verified Patient

“Dr. Culpepper was amazing. He explained things to me that I didn’t understand.”
Verified Patient

“Dr. Sehgal was amazing! Super helpful. She was answering my questions before I even asked. Very happy I picked her.”
Verified Patient

"The appointment went great. It was quick and easy, and the doctor was right on top of things!"
Verified Patient

Reviews shown are from verified LifeMD patients across various services. Photos are for illustrative purposes only.
Asthma is a chronic respiratory condition that affects the airways in the lungs, causing inflammation, narrowing, and increased mucus production, which can lead to symptoms such as wheezing, coughing, chest tightness, and shortness of breath. If you’re experiencing any of these symptoms, it's important to speak with your doctor or a healthcare professional. They’ll take a detailed medical history, conduct a physical exam, and may perform a lung function test using a spirometer.
While asthma cannot be cured, it can be effectively managed with lifestyle changes and the appropriate treatments. Some people may experience a reduction in their asthma symptoms over time, while others may notice their symptoms completely disappear for extended periods but then return.
That being said, it’s essential to continue monitoring and managing asthma symptoms to prevent flare-ups and complications.
An asthma attack is a sudden and severe worsening of asthma symptoms. During an asthma attack, the airways become swollen, inflamed, and narrow, making it difficult for air to move in and out of the lungs. This can cause shortness of breath, wheezing, coughing, and chest tightness.
Asthma attacks can range in severity from mild to life-threatening, and they can be triggered by a variety of factors, including exposure to allergens, exercise, respiratory infections, and stress. If you’ve been diagnosed with asthma, it’s imperative you have an asthma action plan and to seek medical attention immediately if you’re having an asthma attack.
During an asthma attack, the airways become narrowed, making it difficult for air to move in and out of the lungs. This can lead to a decrease in oxygen levels in the body, causing severe symptoms such as shortness of breath, wheezing, coughing, and chest tightness. In some cases, a severe asthma attack can lead to respiratory failure or cardiac arrest, which can be fatal.
Most asthma attacks can be successfully managed with appropriate treatment, including rescue inhalers and oral medications, and by seeking medical attention promptly if symptoms worsen. It’s imperative for those with asthma to have an asthma action plan in place and to seek medical attention immediately if they experience severe symptoms or have difficulty breathing.
No, asthma is not considered an autoimmune disease. It’s a chronic respiratory condition caused by inflammation and narrowing of the airways in the lungs, which can be triggered by a variety of factors. The immune system plays a role in asthma, as it’s involved in the inflammation that occurs in the airways, But asthma is not caused by the immune system attacking healthy tissues, which is the hallmark of autoimmune diseases.
Yes, some studies suggest that genetics can play a role in the development of asthma. If one or both parents have asthma, their children are more likely to develop the condition. However, it’s not entirely clear how genes contribute to its development. Other factors, such as environmental factors and lifestyle choices, can also influence one’s risk of developing asthma.
While some children with asthma may outgrow their symptoms, asthma is generally considered a chronic condition that persists throughout life. However, the severity and frequency of asthma symptoms can vary over time and may improve with the right treatment and management. Some people may experience periods of remission where they have few or no symptoms, while others may continue to experience symptoms despite treatment.
If you’ve been diagnosed with asthma, it’s important to work closely with your healthcare provider to develop a personalized treatment plan and to monitor your symptoms regularly.

Family Medicine
4.93 stars 170 reviews


Internal Medicine
4.98 stars 178 reviews


Internal Medicine
4.92 stars 261 reviews


Family Medicine
4.94 stars 178 reviews


Hormone Specialist
4.92 stars 163 reviews
